Updated: Apr 27, 2025
Author: Tony Waldegrave
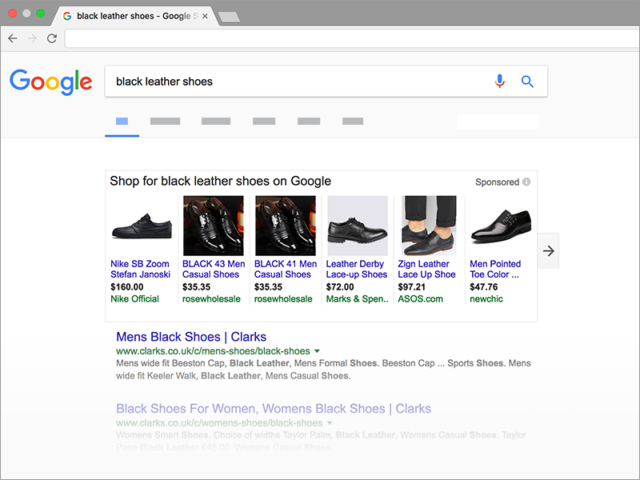
Google Shopping Ads are a powerful way for businesses to showcase products directly at the top of Google Search results.
When someone searches for a tangible product online (like “black leather shoes”), Shopping Ads visually display your products with a photo, price, title, and your business name or website. This makes it easy for potential customers to compare options and click straight through to your site.
Google Shopping campaigns are created through the Google Merchant Center. For New Zealand businesses, this has been available since 2017 and continues to grow in popularity among local online retailers.
Absolutely! Google Shopping Ads feature a product image and a price, so they stand out from the rest of search results.
Google has reported that many businesses discover the click through rates of Google Shopping ads are often 200% to 300% higher than normal text ads. As we will discuss soon, the true success of Google Shopping campaigns largely depends on the quality of your website and how well your campaign is set up and managed.

Without a doubt, all product-based businesses with ecommerce websites should take advantage of the opportunities of Google Shopping.
A significant portion of businesses experience better returns with Google Shopping than with any other ecommerce advertising.
However, much like Google AdWords advertising, Google Shopping campaigns use a complex platform which requires an expert to properly set up and manage. If done right, Google Shopping can be a gold mine. If you haven't got AdWords set up already, we definitely recommend checking out our Google Ads services page.
Like we said earlier, Google Shopping campaigns are set up in the Google Merchant Centre platform. However, you can view your products, manage your bidding, and address certain errors and opportunities for improvement within Google Ads. Within Google Ads, you can also view industry benchmarks to help you understand how you are performing compared with other businesses similar to you (including average click-through-rates, your impression shares, average CPC bids and more).
Here is a simple step-by-step guide:
To ensure you are eligible to run Google Shopping ads to your website, do the following:
Google Shopping works very similar to Google Ads (AdWords), with the exception of how keywords and bidding rules are used. Normal AdWords text ads are targeted using keywords. In Google Shopping, Google automatically targets your products to all relevant searches. To tighten you targeting, you can organise your products into more specific Product Groups. Bids are set at the Product Group level.
When you create a product, you tell Google about your product by giving it Attributes. Product Attributes include a unique Item-ID, a Brand, a product Category (e.g. ‘Apparel & Accessories > Clothing > Dresses’), a Product Type, Custom Labels, product Condition, a distribution/sales Channel, and Channel Exclusivity. So what are these? Product Type is obviously very similar to product Category. However, product categories are predefined by Google, whereas you can custom-set a Product Type if no product Category is able to closely define your product (e.g. ‘Apparel & Accessories > Clothing > Dresses > Maxi Dresses’). Placing Product Groups inside Ad Groups allows you to set negative keywords (to tighten your targeting even more).
For more information, please contact the friendly pros at Adhesion.
Right off the bat, your website needs to be optimised for ecommerce. About two thirds of people who purchase a product via a Google Shopping ad buy a different product from the one they clicked. This is why it is important to feature other similar or popular products on each landing page (maybe try a slider at beneath each product and see the difference it makes).
Next is pricing. It's important to test the price elasticity of your products. For some products, setting your price to $1 less than the prices in your competitors' ads can make a huge difference. For others products whose design/look influences consumers' decisions, a higher price won't impede your click through rates and may also suggest that your product is premium. Either way, it is of paramount importance that the prices in your ads match the prices on your landing pages (otherwise Google can suspend your account, really).
You should also use effective product titles and images. Be descriptive and include keywords in product titles, but keep them under 50 characters to avoid truncation.
MarketingLand.com published an article which suggests that, when setting product Titles, it is better to overpopulate product Titles with keywords rather than under-populate product Titles with keywords. Also, remember to keep your product Titles to 50 characters (including spaces) or less, otherwise they may be cut short in Google Search.
Arguably more important than a product's Title, is its image. Humans are very visual creatures and a high quality, accurate photo will likely give people more information than a product's Title and Description. Product photos should not have any photoshopped logos or borders, and they should not look too different from the product images on your website. The optimal size for a product photo is about 172 pixels by 172 pixels.
You would also want to make sure to get your product feed right. Include accurate product attributes - Item ID, Brand, Google Product Category, Product Type, and more - to help Google place your products in the right searches.
Last but not least, the campaign-level structure of your Google Shopping account is very important. You should create a separate campaign for any products whose category is significantly different to your main products (e.g. one for Dishwashers and another for Microwaves). Splitting vastly different products into multiple campaigns allows you to set Campaign Priorities. You can set different Priorities to each campaign (low, medium or high) that control your bidding preferences. The same product can exist in multiple campaigns but each campaign can have a different bidding strategy. So, for example, you can make a high Priority campaign with a rule that increases your max CPC bid by +10% only for relevant searches made by people aged 35 years or younger. If somebody older performs a search for your product, then the max CPC bid will default to that of the low Priority campaign. However, you need to be careful with placing the same product in multiple campaigns. This is because it is easy to create conflict between the two bids from each campaign’s product, effective putting the products up against each other to compete.
Adhesion helps NZ businesses set up, manage, and get the most out of Google Shopping Ads. For more information or a quote, contact us today.
"We moved to Adhesion from another agency and we have been nothing but impressed with their exceptional service. With Jen and Ricki-lee's support we now have clarity on our strategy and the performance of our campaigns has significantly improved. Jen is a truly dedicated account manager who goes above and beyond for her clients. Highly recommend Bobby, Jen, Ricki-lee, Thomas and the team at Adhesion"
★★★★★ Benedict Stewart January 2026
"Adhesion have consistently provided great service for the past 9 years that I have worked with them. The team is friendly, helpful and knowledgeable. Thank you to Jen, Peter and Courteney for all of your hard work and guidance."
★★★★★ Hayley Blase December 2025
"Working with Jennifer from Adhesion has been a real asset to our business. She’s proactive, reliable, and always focused on helping us achieve better results. I’ve come to trust her judgment and appreciate the way she partners with us to navigate a competitive environment. Having someone like Jennifer on our side gives us confidence that we’re making the right moves to grow our business."
★★★★★ Malcolm Reid December 2025
"Adhesion started managing the Google Add campaigns and profile for The Fantail House stores 3 months ago. Their results have been outstanding for us and the upshot is a good increase in sales volume. They have the perfect characteristics of youth and intelligence that comes with experience to make them very effective players in this competitive space."
★★★★★ Lisa Caughey November 2025
"We have reached out to Adhesion to do an audit on our Social Media ads after the ads created by another agency didn't bring the results we were hoping to see. They provided great well substantiated feedback very quickly and we decided to make the switch. The team worked really hard and have set up our new ads in an incredibly short time frame as we needed to get going to achieve our launch objectives. Within a day of running the new ads we have seen a huge increase in traffic and conversion to our website. Especially Peter Volkov has been incredibly responsive and really great to deal with. We are now expanding our ads and also adding Google Ads to the scope. We are looking forward to seeing more great results. Thanks team!"
★★★★★ Jana Greissner da Silva October 2025
"I couldn't recommend these guys enough. Between Jen, Rueben, Courteney and Alex they've taken our business from complete startup with no Google footprint to a huge amount of great quality converting traffic. They're always on hand no matter how big or small the request is. I've learnt heaps about Google and how best to use it within the business. Thanks Team!"
★★★★★ Alyce Boyle October 2025
"Peter has been fantastic to work with, proactive, clear in his communication, and genuinely focused on getting the best results. Highly recommend his support"
★★★★★ Toby Appleton September 2025
"We have been working with Ricki-lee from Adhesion with our online marketing for a while now and I can tell you she is full of great ideas for getting people interested and contacting our business. In fact, Ricki-lee is now a very important part of our team, and I can't recommend her, and the team behind her, highly enough."
★★★★★ Kevin Downing June 2025
"I've really enjoyed working with Jen and Ryan from Adhesion! They've been very responsive and knowledgeable and have gone out of their way to help when I've needed campaigns setup in short notice. Highly recommend the team at Adhesion!!!"
★★★★★ Karthik Hariharan May 2025
"Very efficient in getting a result."
★★★★★ Oksana Fediuk May 2025
"We've been with Adhesion for a couple of years now, and they've consistently provided prompt and reliable support. Thanks a lot team for your expert advice and exceptional service throughout this time. Our Google Ads have been performing much better in recent months, thanks to your hard work and dedication. Our recent experiences with Ricki-Lee and Jennifer have been fantastic—it’s such a relief to know that we can be in contact anytime we need. It truly feels personal. Thanks again, ladies! 😊"
★★★★★ Sandeep Nagpal May 2025
"I have been with Adhesion for a couple of years and I am very confident that they are working in my best interest. Peter Volkov communicates well with me and picks up concepts about my business quickly. I am doing well in my business as a result of Adhesion's commitment to their client. I previously had an unfortunate experience of working with a large company who promised the world, charged the earth and delivered nothing of value. The difference now is outstanding."
★★★★★ Karen @ Child Behaviour Service April 2025
"Peter has done a great job running my google ads - highly recommended."
★★★★★ Alex Patten April 2025
"Working with Adhesion I have found them to not only be very helpful but also reasonable and fair on pricing"
★★★★★ Rita Patel-Kumar April 2025
"After years of watching clients get burned by faceless agencies and one-person marketers who vanish overnight, finding Phillippa at Adhesion felt like a revelation."
★★★★★ Alex Mann April 2025
"Ricki-Lee was an amazing account manager. Always pro-active and looking for improvements to my campaign. Would highly recommend!"
★★★★★ Chris April 2025
"A huge thank you to Adhesion, and especially to Ricki-lee, for being an absolute rockstar with my ad campaigns! From the very start, she’s been incredibly responsive—always quick to answer any questions and on top of everything to make sure my ads are running smoothly. I love how creative she is, the way she puts the ads together is just perfect! She continuously monitors and optimizes them, making sure they perform at their best. If you're looking for someone who truly cares about your success and delivers amazing results, Ricki-lee is the one!"
★★★★★ Picnique Queenstown February 2025
"I've had the pleasure of working with the Adhesion team for years, and they have consistently provided professional and valuable services. The entire team is fantastic to work with, and Courteney, in particular, stands out for her attentiveness and responsiveness. Her keen attention to detail and dedication to delivering top-quality service have greatly benefited our projects. I highly recommend Adhesion for their expertise, reliability, and outstanding customer support."
★★★★★ Frank Krieger January 2025
"Adhesion, Jen & Court have taken our online marketing strategy from strength to strength over the many years we have been using them for Gordon Harris. Courteney is an absolute star! Their knowledge is deep and broad, keeping us up to date with the latest opportunities to make our campaigns work better. Highly recommend."
★★★★★ Laura Budd January 2025
"I worked with Reuben @ Adhesion through a previous business which was sold and a new start up business of mine. Very prompt at setting up new campaigns, sorting issues and implementing changes. Nothing was ever an issue and all campaigns delivered acceptable results. Would recommend to any small business owner looking for a more personal agency."
★★★★★ Kyle Simpson December 2024
"We love working with the team at Adhesion, they did an outstanding job with our website—The Lodge at 58 North. Not only did they understand our unique needs as small business owners, but they also perfectly blended creativity and functionality, crafting a site that captures the spirit of our lodge while providing an intuitive, user-friendly experience for our guests. The team's attention to detail and expertise brought our vision to life, showcasing our lodge's unique charm and commitment to authentic experiences.The whole team is professional, highly responsive, and genuinely invested in our success—making us feel supported every step of the way. The result is a beautiful, functional website that reflects our lodge and makes it easy for visitors to explore, book, and get excited about their stay.We highly recommend the Adhesion Team—it's a joy to work with them!"
★★★★★ Administrative Assistant October 2024
"I would like to say that Reuben Nel from Adhesion has been of excellent assistance with our google words campaign. He has excellent knowledge and insight and could communicate that in an easy and understandable way. I would certainly recommend Reuben to you"
★★★★★ Leave Calendar October 2024
"We've been working with Courteney from Adhesion for a year now and it's one of the best business decisions we've made. The growth in online sales, as well as in-store referrals, is testament to Courteney’s expertise. Her communication is superb, she offers practical advice, and nothing is a problem. Highly recommend!"
★★★★★ Velo Ronny's Bicycle Store September 2024
"I have been using adhesion for about 2 months now and my ads and revenue has increased significantly, not too mention there customer service is 5 star. I will carry on working with this company and Rueben Thank you for great work. I highly recommend after using many different agency’s over the last 2 years in NZ and AU. Thanks Again James Roberts SPORTZONE"
★★★★★ James August 2024